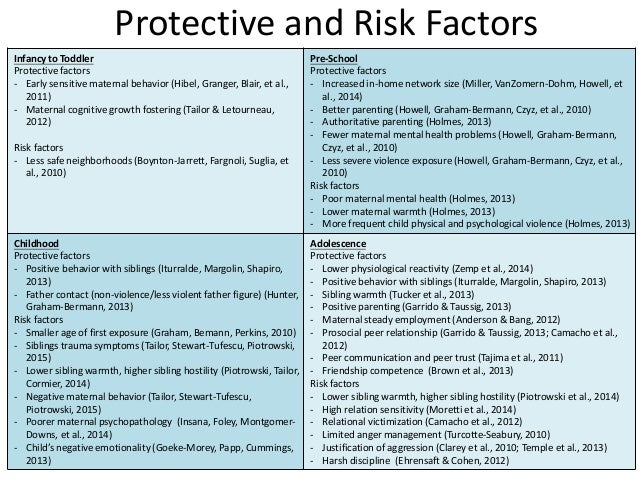
· Adolescent factors examined included demographic and clinical factors (gender, age, residential location, number of mental health problems, experience with online therapies), technology factors (liking, access, confidence), knowledge of online therapies, mental health attitudes, and personality factors (extraversion, agreeableness, conscientiousness, neuroticism, openness) · “Cultural Influences on Mental Health” is part one of a two-part series on viewing mental health from a public health perspective. To read part two, click here.. People often think of mental health as a very personal matter that has to do only with the individual Today we have with us Zach Schleien, Co-founder of Filter Off. Zach has a passion for helping others achieve their goals in the personal branding and mental health space. His journey has been one of successes and failures. He has learned from working on his own side projects as well as working in a corporate setting, now at Johnson & Johnson
Learn About Mental Health - Mental Health - CDC
Mental health includes our emotional, psychological, and social well-being. It affects how we think, feel, and act. It also helps determine how we handle stress, relate to others, and make healthy choices. Although the terms are often used interchangeably, poor mental health and mental illness are not the same things.
A person can experience poor mental health and not be diagnosed with a mental illness. Likewise, online dating mental health factors, a person diagnosed with a mental illness can experience periods of physical, mental, and social well-being. Mental and physical health are equally important components of overall health.
Mental illness, especially depression, increases the risk for many types of physical health problems, particularly long-lasting conditions like stroke, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease. Similarly, the presence of chronic conditions can increase the risk for mental illness. When the demands placed on a person exceed their resources and coping abilities, their mental health could be impacted. For example, if someone is working long hours, Cdc-pdf caring for an ill relative or experiencing economic hardship they may experience poor mental health.
There is no single cause for mental illness. A number of factors can contribute to risk for mental illness, such as. People can experience different types of mental illnesses or disorders, and they can often occur at the same time.
Mental illnesses can occur over a short period of time or be episodic. This means that the mental illness comes and goes with discrete beginnings and ends. Mental illness can also be ongoing or long-lasting. There are more than classified External types of mental illness.
Some of the main types of mental illness and disorders are listed below; however, this list is not exhaustive. People with anxiety disorders respond to certain objects or situations with fear and dread or terror. Anxiety disorders include generalized anxiety disorder, social anxiety, panic disorders, and phobias. It can continue through adolescence and adulthood. People diagnosed with ADHD may have trouble paying attention, controlling impulsive behaviors may act without thinking about what the result will beor be overly active.
Behavioral disorders involve a pattern of disruptive behaviors in children that last for at least 6 months and cause problems in school, at home, and in social situations. Behavioral symptoms can also continue into adulthood. While bad moods are common, and usually pass in a short period, people suffering from mood disorders live with more constant and severe symptoms.
People living with this mental illness find that their mood impacts both mental and psychological well-being, nearly every day, and often for much of the day. It is estimated that 1 in 10 adults suffer from some type of mood disorder, with the most common conditions being depression and bipolar disorder.
With proper diagnosis and treatment, most of those living with mood disorders lead healthy, online dating mental health factors, normal and productive lives. If left untreated, this illness can affect role functioning, quality of life and many long-lasting physical health problems such as diabetes and heart disease.
People with personality online dating mental health factors have extreme and inflexible personality traits that cause problems in work, school, or social relationships. Personality disorders include antisocial personality disorder and borderline personality disorder. A person can get PTSD after living through or seeing a traumatic event, such as war, a hurricane, physical abuse, or a serious accident. PTSD can make someone feel stressed and afraid after the danger is over.
People with PTSD may experience symptoms like reliving the event over and over, sleep problems, become very upset if something causes memories of the event, constantly looking for possible threats, and changes in emotions like irritability, outbursts, helplessness, or feelings of numbness. They may also show signs of disorganized thinking, confused speech, and muddled or abnormal motor behavior. An example of a psychotic disorder is schizophrenia. People with schizophrenia may also have low motivation and blunted emotions.
Substance use problems can be fatal to the user or others. Examples include drunk driving fatalities and drug overdoses.
Mental illnesses and substance use disorders often occur together. Sometimes one disorder can be a contributing factor to or can make the other worse. Sometimes they simply occur at the same time.
Preventing mental illness and promoting good mental health involves actions to create living conditions and environments that support mental health and allow people to adopt and maintain healthy lifestyles.
These include a range of actions to increase the chances of more people experiencing better mental health, such as Skip directly to site content Skip directly to page options Skip directly to A-Z link Skip directly to A-Z link Skip directly to A-Z link. Mental Health. Section Navigation. Facebook Twitter LinkedIn Syndicate. Learn About Mental Health Minus Related Pages. Mental Health Basics Types of Mental Illness Fast Facts What is mental illness? What is mental health? Why is mental health important for overall health?
How common online dating mental health factors mental illnesses? Mental illnesses are among the most common health conditions in the United States. A number of factors can contribute to risk for mental illness, such as Early adverse life experiencessuch as trauma or a history of abuse for example, child abuse, sexual assault, witnessing violence, etc.
Experiences related to other ongoing chronic medical condition Cdc-pdfonline dating mental health factors, such as cancer or diabetes. Biological factors, such as genes or chemical imbalances in the brain Use of alcohol or recreational drugs Having few friends Having feeling of loneliness or isolation.
Anxiety Disorders People with anxiety disorders respond to certain objects or situations with fear and dread or terror. Disruptive Behavioral Disorders Behavioral disorders involve a pattern of disruptive behaviors in children that last for at least 6 months and cause problems in school, at home, and in social situations.
Depression and Other Mood Disorders While bad moods are common, and usually pass in a short period, people suffering from mood disorders live with more constant and severe symptoms. Eating Disorders Eating disorders involve obsessive and sometimes distressing thoughts and behaviors, including Reduction of food intake Overeating Feelings of depression or distress Concern about weight, body shape, poor self-image Common types of eating disorders include anorexia, bulimia, and binge eating.
Online dating mental health factors Disorders People with personality online dating mental health factors have extreme and inflexible personality traits that cause problems in work, school, or social relationships.
Posttraumatic Stress Disorder PTSD A person can get PTSD after living through or seeing a traumatic event, such as war, a hurricane, physical abuse, or a serious accident. Mental Illness and Adults Inthere were an estimated and the 2nd leading cause of death among people aged for both youth and adults aged 18 to adults living with serious mental illness die on average 25 years earlier than others, largely due to treatable medical conditions, online dating mental health factors.
These include a range of actions to increase the chances of more people experiencing better mental health, such as 15 Early childhood interventions for example, home visits for pregnant women and programs that help young children build social and emotional skills.
Social support for elderly persons. Programs targeted to people affected by disasters or other traumatic events, online dating mental health factors. Mental health interventions at work for example, stress prevention programs. Violence prevention s trategies for example, reducing violence in the community and the home.
Campaigns to change online dating mental health factors culture of mental health so that all of those in need receive the care and support they deserve. Strengthening Mental Health Promotion External. Fact sheet no.
Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization. Bethesda, MD: National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Mental Health. Kessler RC, Angermeyer M, Anthony JC, et al. World Psychiatry. Key substance use and mental health indicators in the United States: Results from the National Survey on Drug Use and Health, online dating mental health factors. Rockville, MD: Center for Behavioral Health Statistics and Quality. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration.
Merikangas KR, He J, Burstein M, online dating mental health factors, et al. Lifetime Prevalence of Mental Disorders in US Adolescents: Results from the National Comorbidity Study-Adolescent Supplement NCS-A. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. Bethesda, MD: National Institute of Mental Health. National Institutes of Health.
Kessler RC, Chiu WT, Demler O, Online dating mental health factors EE. Prevalence, Severity, and Comorbidity of Twelve-month DSM-IV Disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication NCS-R.
Archives of general psychiatry. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, Center for Behavioral Health Statistics and Quality. Rockville, MD. Rui P, Hing E, Okeyode T. National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey: State and National Summary Tables. Cdc-pdf Online dating mental health factors, GA: National Center for Health Statistics.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Web-based Injury Statistics Query and Reporting System WISQARS. Atlanta, GA: National Center for Injury Prevention and Control.
How Dating Apps Can Affect Your Mental Health, According To Experts
· “Cultural Influences on Mental Health” is part one of a two-part series on viewing mental health from a public health perspective. To read part two, click here.. People often think of mental health as a very personal matter that has to do only with the individual · Mental health is a state of balance, both within and with the environment. Physical, psychological, social, cultural, spiritual and other interrelated factors participate in producing this balance. There are inseparable links between mental and physical health. More than million people suffer from mental health disorders in the Western · Criminal Behaviour and Mental Health. Volume 26, Issue 4 p. Special Issue Article. based on 10 risk factors, significantly predicted dating violence. Conclusion. Risk factors from four domains were important in predicting dating violence, but
Keine Kommentare:
Kommentar veröffentlichen